Background: The pandemic of COVID-19 affected many countries around the world and Iran was no exception. The aim of this study was to evaluate the health anxiety of the Iranian pregnant women during the pandemic of the COVID-19.
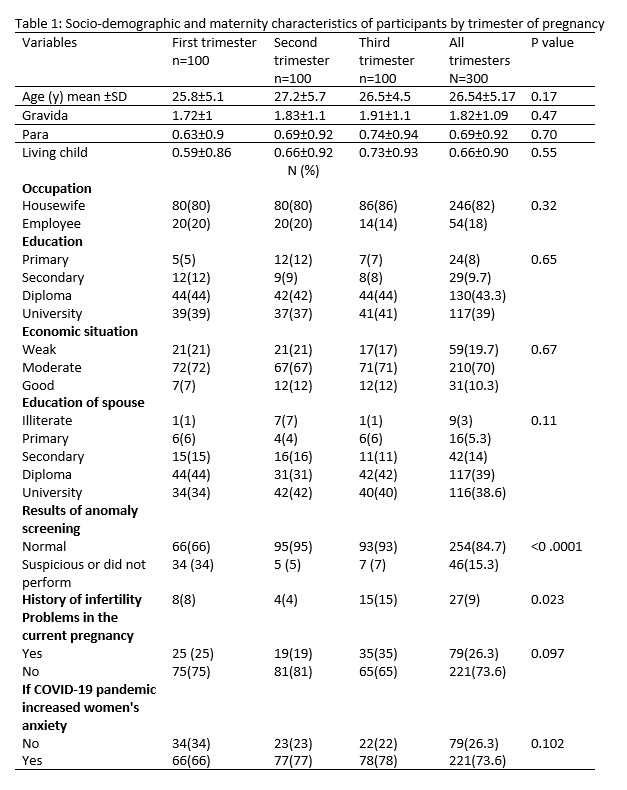
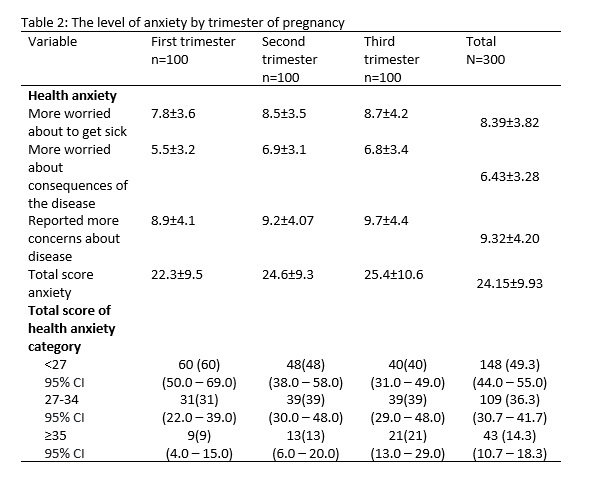
Methods: In this cross-sectional study, 300 pregnant women in different trimesters (n=100 in each trimester) were recruited. A demographic questionnaire and the Health Anxiety questionnaire were used to collect the data. The total score < 27 of means low health anxiety, scores between 27-34 mean moderate health anxiety, and scores more than 35 means high health anxiety. Due to nationwide restrictions, data were collected through social media groups. The chi-square, ANOVA and multiple linear regression were used to analyze the data.
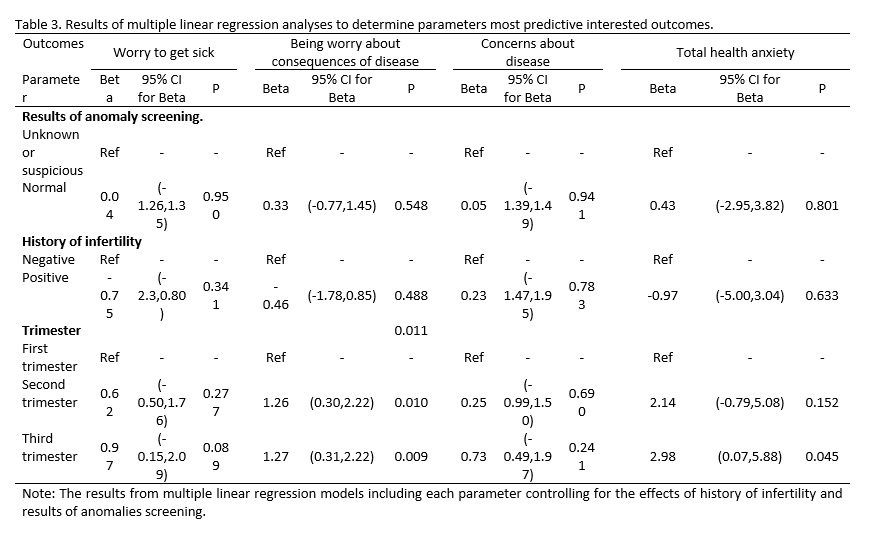
Results: The total score of anxiety was 22.3±9.5, 24.6±9.3 and 25.4±10.6 in the first, second and third trimester of pregnancy, respectively. Particularly, 9%, 13% and 21% of the women had severe anxiety or scores≥35 in the first, second and third trimester of pregnancy respectively. Pregnant women in the third trimester had significantly higher health anxiety score and higher scores of “total health anxiety” than did those in the first trimester (p=0.045).
Conclusion: At the time of the pandemic of COVID-19, women in the second and third trimester of pregnancy were more worried about consequences of disease, but the total score of health anxiety was significantly higher among women in the third trimester of pregnancy. Health care providers should pay more attention to the mental health of pregnant women in times of crises such as Corona pandemic.