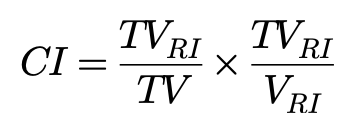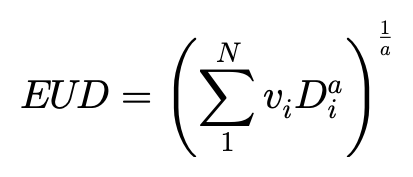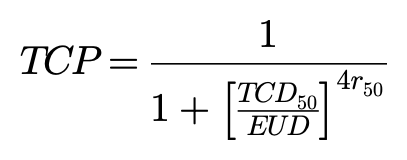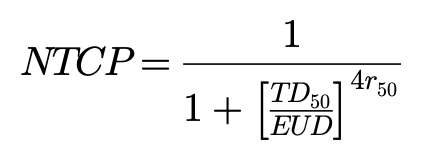Patients and Treatment Planning
Approved 66 NPC patients with SIB IMRT plans were analyzed retrospectively, 16 of whom had high-risk lymph nodes. This study was approved by the medical ethics committee of second affiliated hospital of army medical university, PLA. (2021-Research No. 038-01)
Computer tomography (CT) images were acquired on a Philips Brilliance Big Bore CT scanner (Philips, Cleveland, OH, USA), the slice thickness was 3 mm. Nasopharynx gross tumor volume (GTVnx), lymph node gross tumor volume (GTVnd), clinical target volume (CTV1, CTV2) were delineated. CTVnd was obtained by GTVnd expansion when the lymph nodes were the high-risk region. CTV1 referred to the outward expansion of GTVnx by 0.5 ~ 1.0cm in the front, the upper, the lower, and the sides, and 0.3 ~ 0.5cm in the back (the appropriate distance of outward expansion was determined by the tumor involvement and the distance between the tumor and the spinal cord, brainstem, and other tissue structures). CTV2 consisted of two parts. One was CTV1 enlarged by 0.5 ~ 1.0cm in the front, the upper, the lower, and the sides, and then enlarged by 0.3 ~ 0.5cm (the appropriate distance is determined according to the tumor involvement and the distance between the tumor and the spinal cord, brain stem, and other tissue structures). The other was GTVnd, its lymphatic drainage area, and the negative lymphatic drainage area requiring prophylactic irradiation. The planning target volume (PTV) was created based on each target volume with an additional 3mm margin, considering setup variability.
The prescription dose to PGTVnx, PGTVnd, PCTV1, PCTV2 were 69-72Gy, 60-70Gy, 60-64Gy, 50-56Gy in 30-33 fractions, respectively. When the lymph nodes were the high-risk region, the prescription dose to PGTVnx, PGTVnd, PCTVnd, PCTV1, PCTV2 were 70Gy, 66-70Gy, 60Gy, 60Gy, 54Gy in 33 fractions, respectively. Critical organs at risk, including the brain stem, spinal cord, lens, optic nerve, optic chiasma, parotid gland, were also contoured by the certified oncologist.
All IMRT plans were generated using the Eclipse planning system (Varian Medical System, Palo Alto, CA) with 120 MLC. The Anisotropic Analytical Algorithm (AAA, version 15.6.06) dose calculation algorithm was chosen for dose calculation using the dose calculation grid resolution of 0.25×0.25×0.25cm3. The treatment couch was not considered in the dose calculation. All cases used nine equally spaced beams for IMRT sliding window plans. The collimator rotation and jaw positions were optimized and fixed by the dosimetrists.
A new target autocrop function was introduced in the Varian Eclipse TPS to handle the overlapping targets volume. The principle diagram was shown in Fig.1. After activating the target autocrop function, TPS automatically identified the target areas with contradictory doses objective and overlapping areas, such as PGTV and PCTV in Fig.1(a), which required different prescription doses. Then, a 5mm buffer ring between the PGTV and PCTV would be formed, and the optimization and calculation for the PCTV would be carried out automatically according to the shaded area in Fig.1(b).
The manual cropping plans, which oncologists had been accepted and approved, served as reference. Reference plans were re-optimized with identical planning optimization parameters and OAR constraints following the institutional clinical protocol except for the optimization objective of the manual cropping targets deleted. Additionally, each target had one lower objective at 100% volume and one upper objective at 0% volume for the autocrop plans.
All plans were performed on a Varian Trilogy linear accelerator, which adopted 6 MV photon and a sliding-window technique. The accelerator is equipped with a multi-leaf collimator containing 120 leaves, 80 5.0 mm central leaves, and 40 10.0 mm peripheral leaves.
Plan Quality Evaluation
The treatment plan was evaluated by multiple parameters, which included target coverage criteria, normal tissue sparing criteria, biological parameters TCP and NTCP, treatment efficiency, as well as accuracy. The paired t-tests were performed to assess statistically significant differences (p < 0.05).
In terms of target coverage criteria, PTV dose-volume histogram (DVH) parameters, including D2%, D98%, Dmean, HI (homogeneity index), CI (conformal index), were computed and recorded with the ICRU83 report[12], defined as follows:

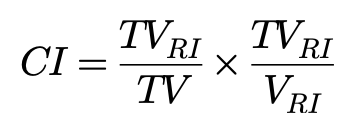
Where RI represents the prescribed dose, TVRI is the volume of target covered by prescribed dose, TV is the target volume, and VRI is the volume of the body covered by prescribed dose. Variables were assessed for organs at risk (OARs), including mean dose (Dmean), maximum dose (or point in a significant volume, Dmax or D1), volume receiving a fixed-dose level, and dose levels delivered to a certain volume.
Radiation biological parameters tumor control probability (TCP) and normal tissue complication probability (NTCP) were calculated from the extracted differential dose volume histogram (DVH) data based on the Niemierko model.[13,14]
The equivalent uniform dose (EUD) was calculated by:[15]
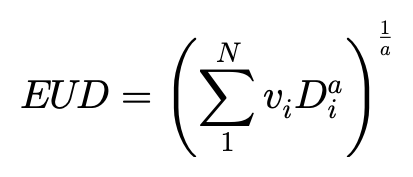
where Vi is fractional volume, Di is dose bin, and a value is the tumor normal tissue-specific parameter that describes the dose-volume effect. For NPC cases, “a” value is -13.[16,17] The TCP could be calculated based on the equivalent uniform dose: [18]
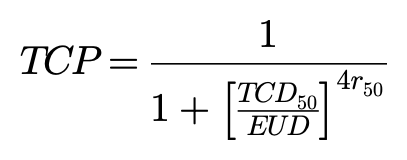
where TCD50 is the tumor dose required for producing 50% TCP and r50 is the slope of dose response at 50% TCP. Okunieff et al[19]reported that tumor-specific parameters for head and neck squamous cell (macroscopic) were TCD50=51.77Gy, r50=2.28. Also, the NTCP was determined below:
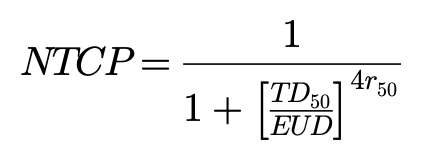
where TD50 is the dose at which probability of complication becomes 50% in 5 years and r50 is the slope of sigmoidal dose response curve of normal tissue at 50% complication probability. These specific parameters given for normal tissue were based on the reports of Emami et al[20] and Burman et al[21](Table 1).
Table 1 Specific parameters given for normal tissue based on the reports of Emami et al.[19] and Burman et al.[20]
|
Stucture
|
Endpoint
|
a
|
r50
|
TD50 (Gy)
|
|
Brainstem
|
Necrosis
|
7
|
3
|
65
|
|
Spinal cord
|
Myelitis/necrosis
|
7.4
|
4
|
66.5
|
|
Optic chiasm
|
Blindness
|
25
|
3
|
65
|
|
Optic nerve
|
Blindness
|
25
|
3
|
65
|
|
Lens
|
Cataract
|
3
|
1
|
18
|
|
Parotid
|
Xerostomia
|
5
|
6
|
46
|
The dose delivery efficiency of each plan was evaluated based on the total number of MU, which were compared between the autocrop plan and the manual cropping plan. Additionally, the agreement of the planning and delivered doses was assessed by studying the patient-specific QA results. The QA of the auto-crop plan and the manual cropping plan was performed with PTW seven29, and the gamma passing rates were compared. The criteria for gamma analysis was 3%/3mm, with a 10% dose threshold.